Applied units
Специалността инженерна химия и съвременни материали има за цел да съчетае The Chemical Engineering and Contemporary Materials program combines theoretical learning and the acquisition of practical skills, which will help graduates who work in the field of industrial chemistry. For this reason, the program includes units that help put the previously acquired knowledge in practice.обучение с придобиване на практически умения, необходими за успешна реализация в индустриалната химия. Поради тази причина в програмата на специалността са заложени курсове, които са насочени към прилагането на получените знания от предишни курсове в практиката.
Units from this Section
Unit Operations of Chemical Technologies
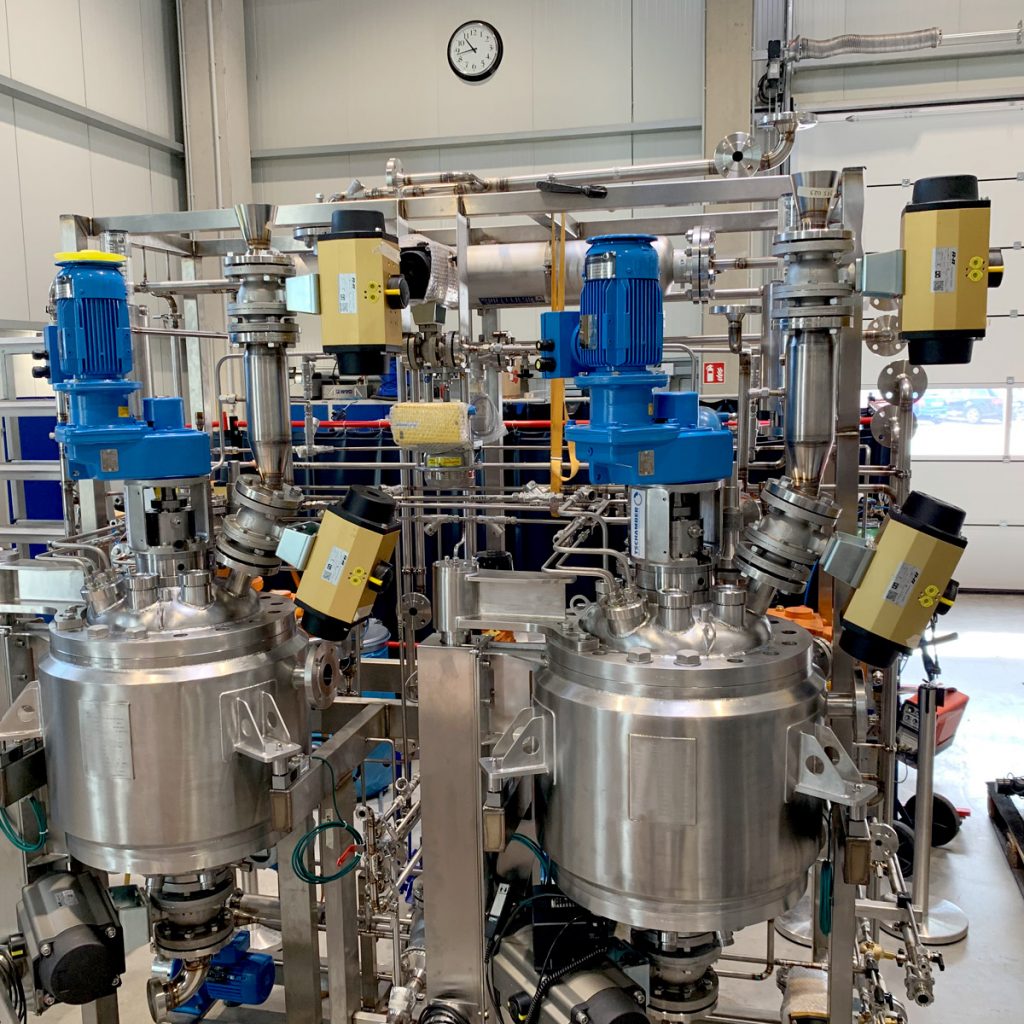

The unit aims to teach students the basic processes, apparatus, and machines in chemical technology. The main characteristics of the processes of transfer and separation in a chemical manufacture, their aspects and/or ways and manners of proceeding are detailed. The basic characteristics of different commonly used industrial machines are presented to help students understand how to properly select and use them, as well as to illustrate what important technological parameters affect the shape and dimensions of the machine.
The purpose of the lab practice is to gain practical experience in working with data, to compile balance dependencies, and above all to determine and make an estimate of important technological parameters in the processes.
Engineering graphics
In Engineering Graphics classes, students get familiar with the basics of modern engineering design. The exercises include an introduction to basic elements of descriptive geometry – types of views, projections, and engineering graphic formats, using 3D software for designing details for machines and devices used in production. In the practical exercises, students will gain the ability to read production schemes of various devices and technological equipment.
Chemical technologies
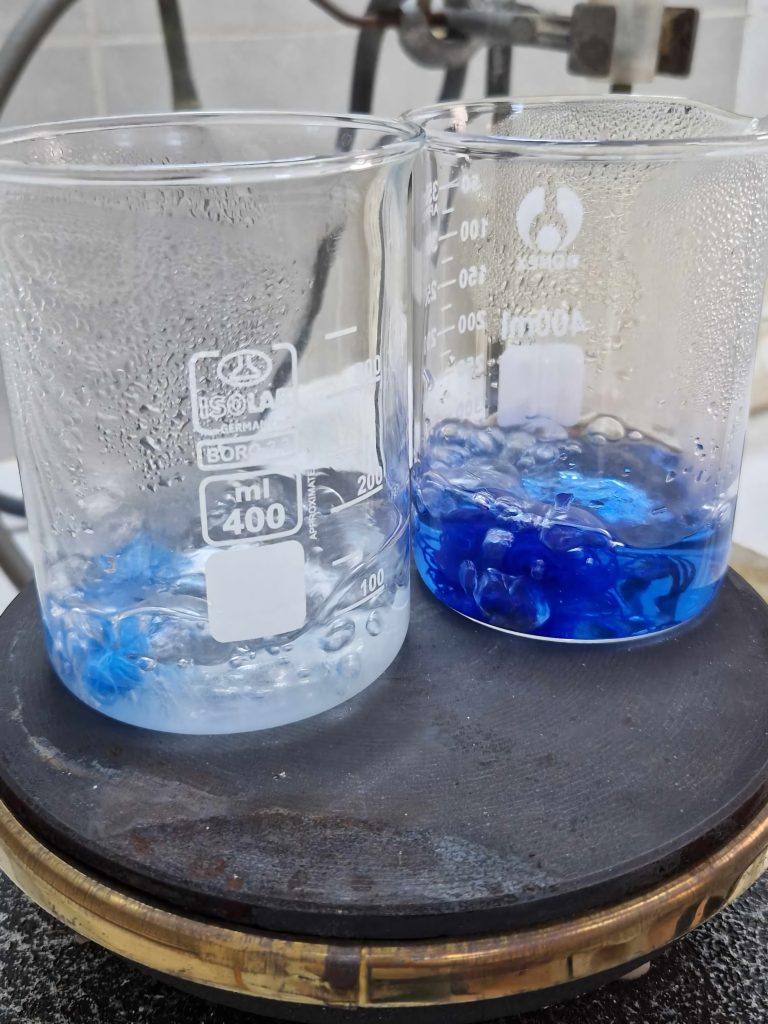

The chemical technology unit will introduce you to the production world of various materials and raw materials. You will study the methods and machines used in industrial processes, and consider the chemical and physical factors that affect them. The unit pays attention to the production of some inorganic industrial chemicals - acids and bases, fertilizers, and metallurgy - as well as some organic chemicals - related to the pharmaceutical industry, the production of dyes, aromatic substances, and others. The unit lab practice will show you how to control a technological process. You will also deal with the synthesis of some substances, for example dyes, with which you will be able to dye fabrics!


Applied Electrochemistry
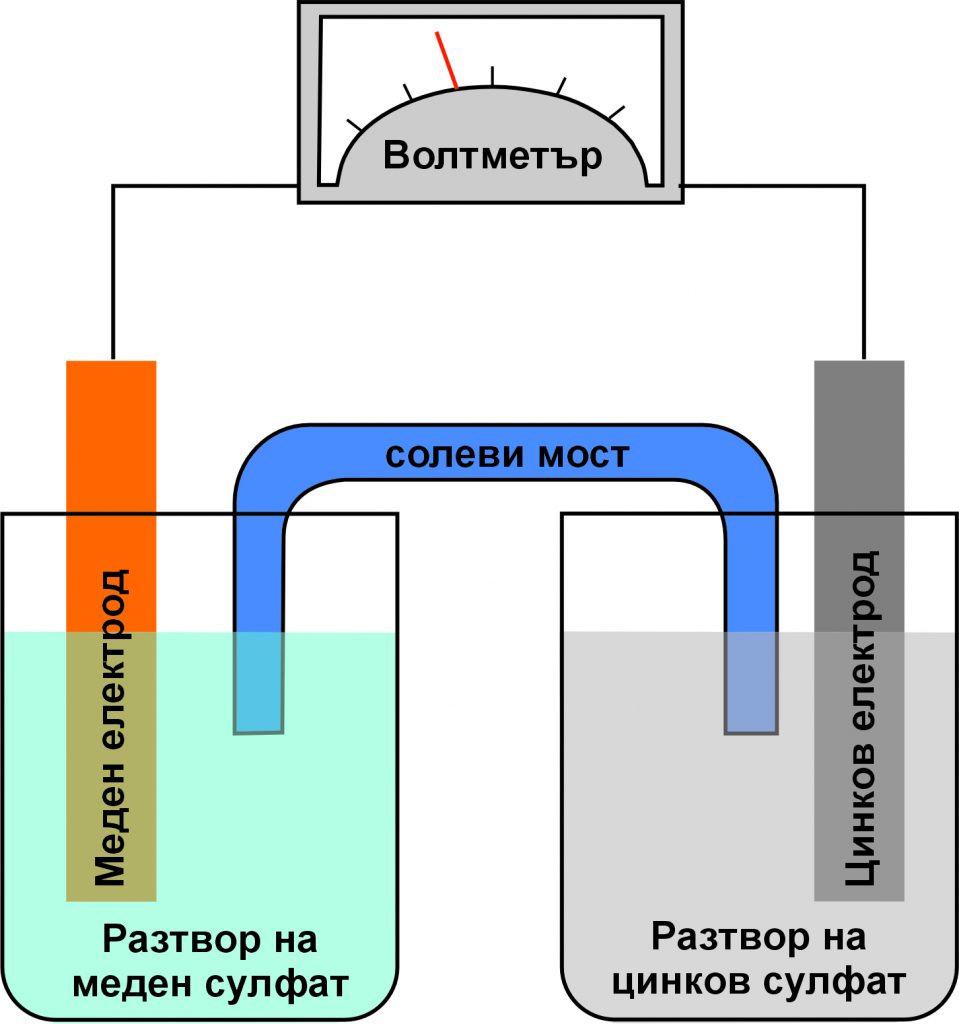
In the Applied Electrochemistry unit, you will have the opportunity to learn about the relationship between electricity and chemical processes – namely how we can use electricity to control chemical reactions.
You will learn about the behavior of electrolytes in solutions and the property of electrical conductivity. You will learn what a galvanic cell is, and how it is used to make the modern lithium-ion batteries that are used in our daily lives such as in phone batteries, electric cars, and more. You will learn how an oxidation-reduction process can be used to obtain the surface coating of materials from precious materials (gold plating), as well as to construct passivating coatings that aim to protect the material from corrosion.
Thermodynamics
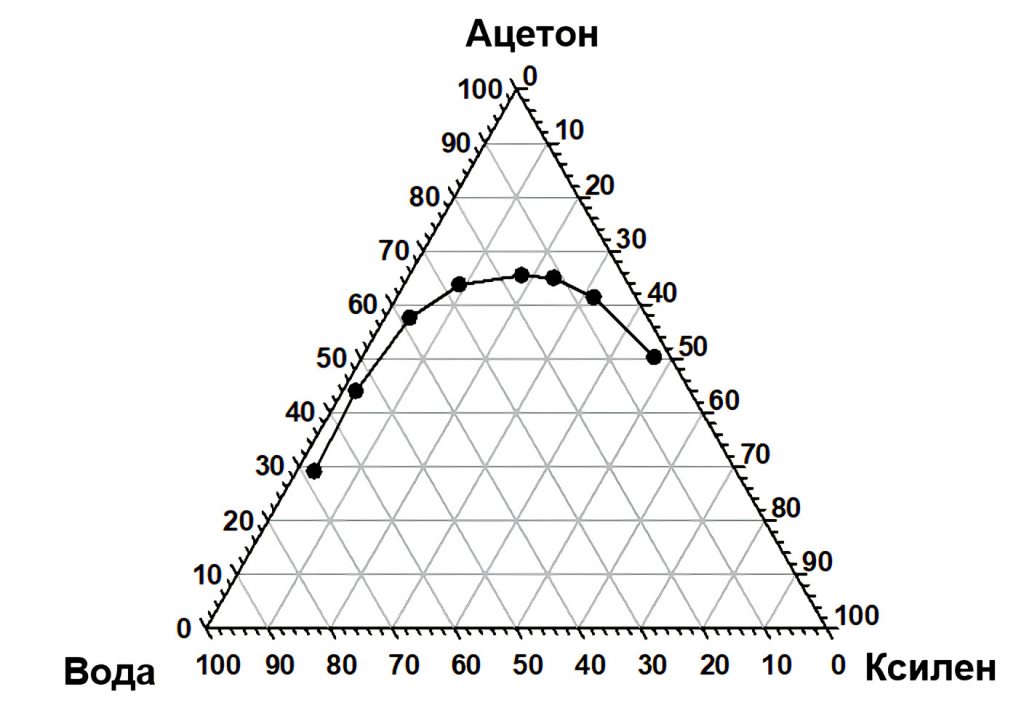
The unit introduces basic concepts that are essential for the control of processes involved in various industries related to chemical engineering and materials science. The theoretical aspects of homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions are studied, as well as the main types of interactions occurring in solutions - van der Waals, solvation processes, hydrogen bond formation. The mechanisms of macroscopic phenomena such as phase separation (when water does not mix with oil) and phase transition (melting, crystallization, etc.) are explained, in relation with intermolecular interactions. The lab practice reinforce the acquired theoretical knowledge. One of the practical classes shows how intermolecular interactions and environmental conditions (such as temperature, for example) affect the solubility of a given substance. For instance, water and xylene do not mix well, but by adding acetone we can improve the solubility of xylene in water. Above the so-called binodal curve presented in the figure, we observe a homogeneous solution, and below it – separation of a layer of xylene.
Visit of manufacturing industries
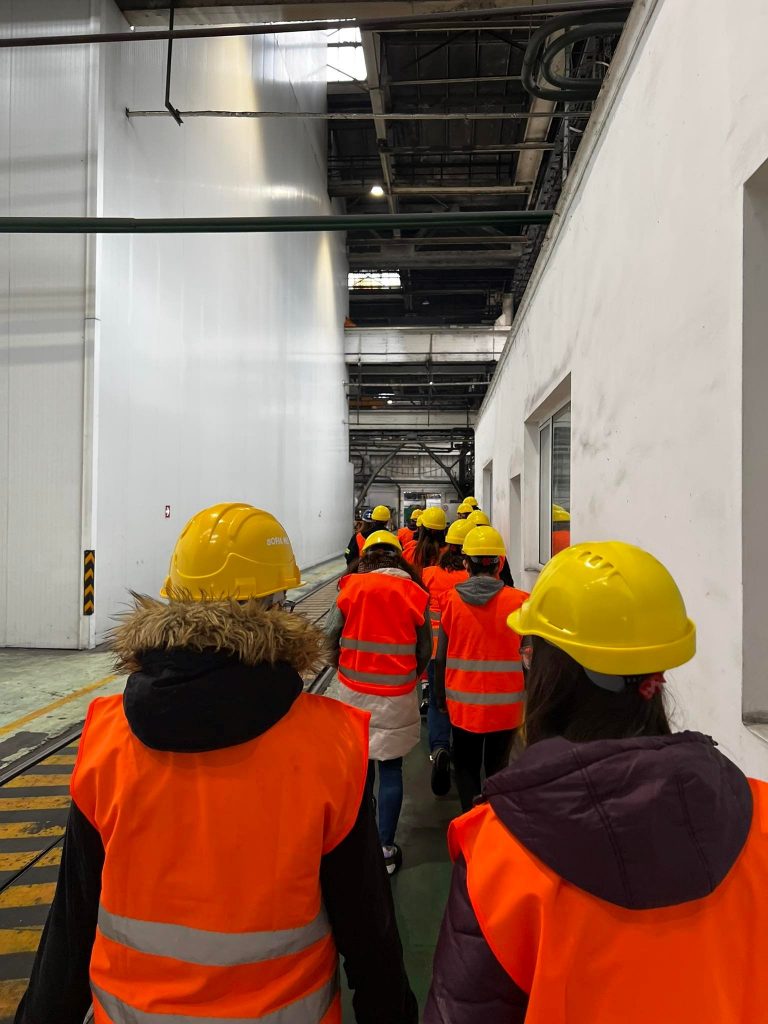

The unit aims to acquaint students with the technologies and processes that are carried out in various production enterprises, such as the production of acids, bases, technical salts, metallurgy, and products from the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries. Visiting factories allows students to see how the processing and quality control of raw materials are carried out in practice, and how a target product is obtained from them. This allows deepening the knowledge of process control obtained in the chemical technology unit, but also gives the opportunity to contact potential future employers.
More about the practical training