Fundamental units
The units in this section are important as they go deeper into the different areas of chemistry. They can commonly be divided into theoretical and applied. Theoretical units provide knowledge of the basic principles in the studied disciplines, and applied units show how and where these principles are used in practice.
Units from this Section
Analytical Chemistry
The Analytical Chemistry unit will give you the basic knowledge you need to perform quantitative and qualitative analysis of chemical substances in a sample. The stages of the analysis include taking a sample, preparing the sample for analysis, choosing an analytical method, and summarizing the results obtained. You will also learn some basic quantification methods – those based on acid-base interactions and complexation, and those involving an instrument during the analysis (e.g., molecular spectra analysis). In a large part of the lab practice, you will deal with titration - a simple laboratory experiment through which you will be able to determine the concentration of a substance in a solution.
Analytical chemistry can give us answers to questions such as: what do we call the 'hardness' of water? As we all know, water contains a number of different ions. The hardness of water depends on the concentration of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions in it. That's the exact topic of one of the exercises where the hardness of several water samples taken from different parts of Bulgaria is compared"
Inorganic Chemistry
Inorganic chemistry studies the synthesis methods and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This branch of chemistry has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry – catalysts, materials, coatings, fuels, and agriculture. In the unit, you will get to know the elements of the periodic table in detail by looking at the chemical and physical properties of their elementary substances.
During the laboratory practice, you will have the opportunity to use experimental set-ups such as one used for obtaining oxygen and hydrogen, gases of extreme importance for our planet. You will learn about the mechanisms of the reactions and what conditions are needed to conduct them.
During the laboratory practice, you will have the opportunity to use experimental set-ups such as one used for obtaining oxygen and hydrogen, gases of extreme importance for our planet. You will learn about the mechanisms of the reactions and what conditions are needed to conduct them.
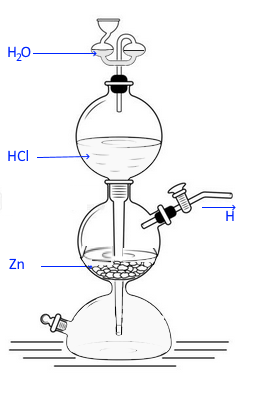
"Апаратът на Нойман се използва за получаване на газове в голямо количество. През горния отвор внимателно се поставят гранули цинк (Zn). При затворен кран от страничния отвор, с помощта на фуния се налива сярна киселина. Кранът се отваря, при което се осъществява взаимодействието между киселината и цинковите гранули. Отделеният водород се събира в епруветка с отвора надолу чрез изместване на въздух. При поднасяне на пламък се осъществява запалването му, което доказва и получаването му."
Physical Chemistry

In the Physical chemistry units, chemical interactions are studied based on the main principles of physics (such as energy, force, time, etc.), with a mathematical model for their description. The main topics of physical chemistry are related to the study of the structure and properties of matter, as well as the thermodynamics of chemical reactions, phase transitions (melting, crystallization, etc.), electrochemical processes, and surface phenomena. The unit provides basic knowledge in the field of thermodynamics and kinetics of chemical reactions, which are key to mastering further units such as disperse systems and chemical kinetics.
"Phenomena that we see in our daily life can be explained by the laws of physical chemistry, such as: why do bubbles of gas come out of our carbonated drink after we open the can? This phenomenon is explained by the Henry principle - the amount of gas that will dissolve in a liquid increases as the pressure increases. The pressure in a closed container is higher than atmospheric, so when it is opened, the dissolved gas begins to escape in the form of bubbles. "
Structure of Matter
The Structure of Matter unit teaches basic concepts and theories used in the description of the structure of atoms and molecules, whose properties are determined by electrons. Therefore, emphasis is placed on the electronic structure of atoms and molecules, and ideas from quantum mechanics. The nature of the chemical bond between the atoms as well as the molecular structure are just as important, as they also determine the properties of substances. Some of the material’s properties are explained, such as why different materials and substances have color and why others, under certain conditions, can glow, what makes a substance capable of conducting an electric current, or what determines magnetic properties.
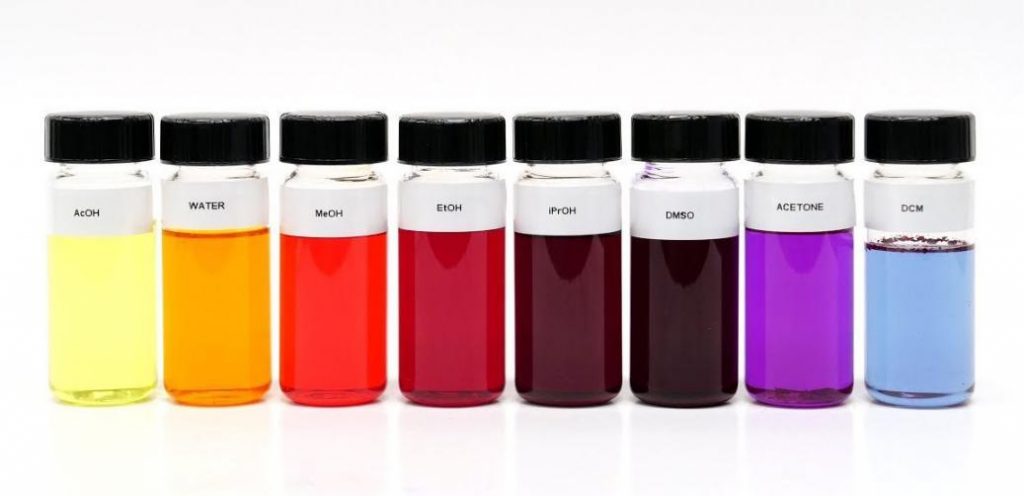

"Solutions of the same substance in a different solvent are shown. The nature of the solvent has a visible effect on the properties of the substances, changing the solutions’ color. The concept is called solvatochromism."
Organic chemistry
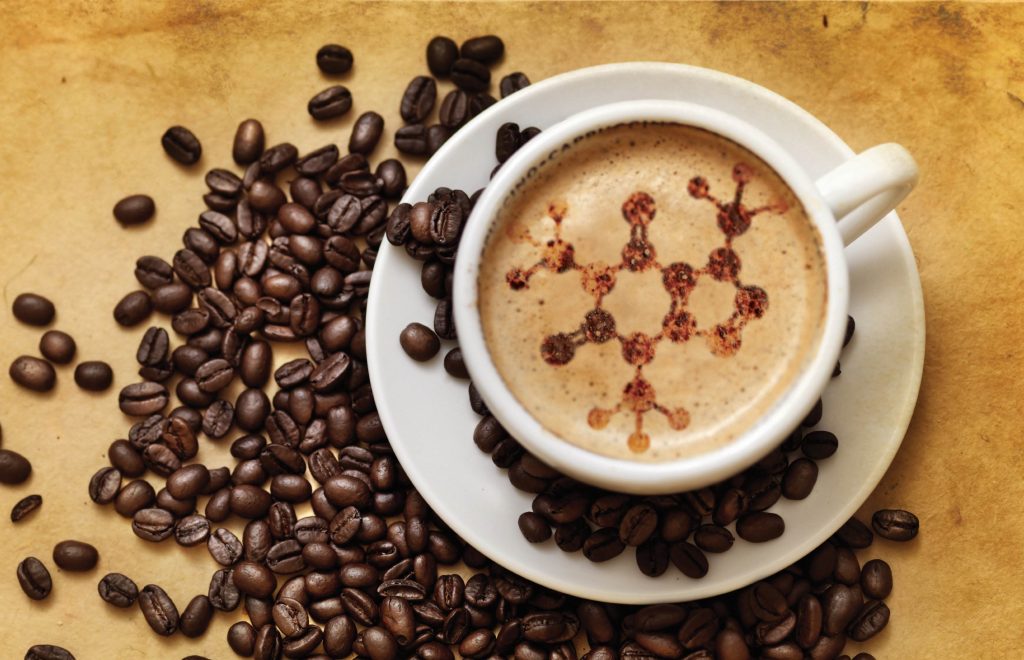

In Organic Chemistry units, you will study the main classes of organic compounds, divided by functional groups. Examples are not given in terms of very complex macromolecules, but rather simpler or more general formulas. The aim of the unit is to build an understanding of the basic properties of a given functional group, and what possible reactions different molecules can participate in depending on what groups they contain.
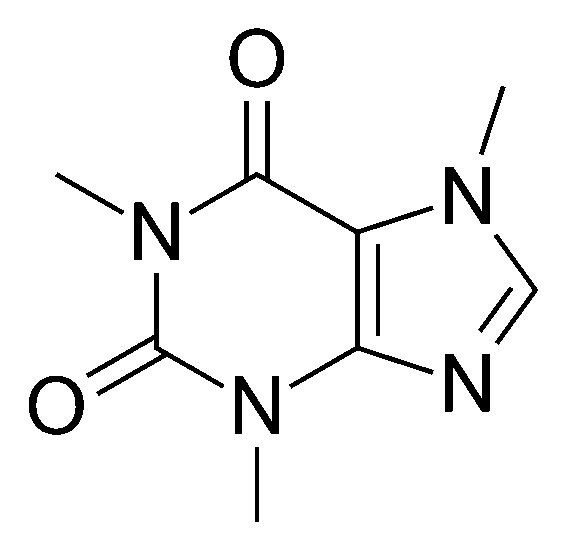
"All living organisms are composed of organic compounds, also known as carbon-containing compounds. Examples of such molecules are proteins, enzymes, hormones, and poisonous compounds in various animals and plants. Organic compounds are also found in non-living matter - these are dyes, many polymers, as well as some of the ingredients in medicines and foods. That is why the study of organic chemistry is extremely valuable to mankind. With its help, biochemical reactions are described and compounds unknown to mankind are synthesized. The image shows the structural formula of a substance among one of the most widely consumed by humans - caffeine. It is found naturally in coffee, tea, and chocolate."